Atlı stated that Africa has great needs for development, especially infrastructure, and that China stands out due to its ability to meet these needs under the most favorable conditions.
As part of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China is increasing its economic and strategic influence on the African continent and strengthening its position in global trade. Announced in 2013, the BRI aims to build a vast infrastructure network stretching from China to Asia, Europe and Africa. Large-scale projects such as railways, ports, highways and power plants are the cornerstones of this initiative.
African countries have become an important part of these projects with billions of dollars in Chinese loans, while institutions such as China Exim Bank and China Development Bank play a critical role in financing the projects. However, this situation brings with it controversy in the international arena. Experts are concerned that Chinese loans could lead some African countries into a “debt trap”. There is a lack of transparency and questions about the sustainability of some projects.
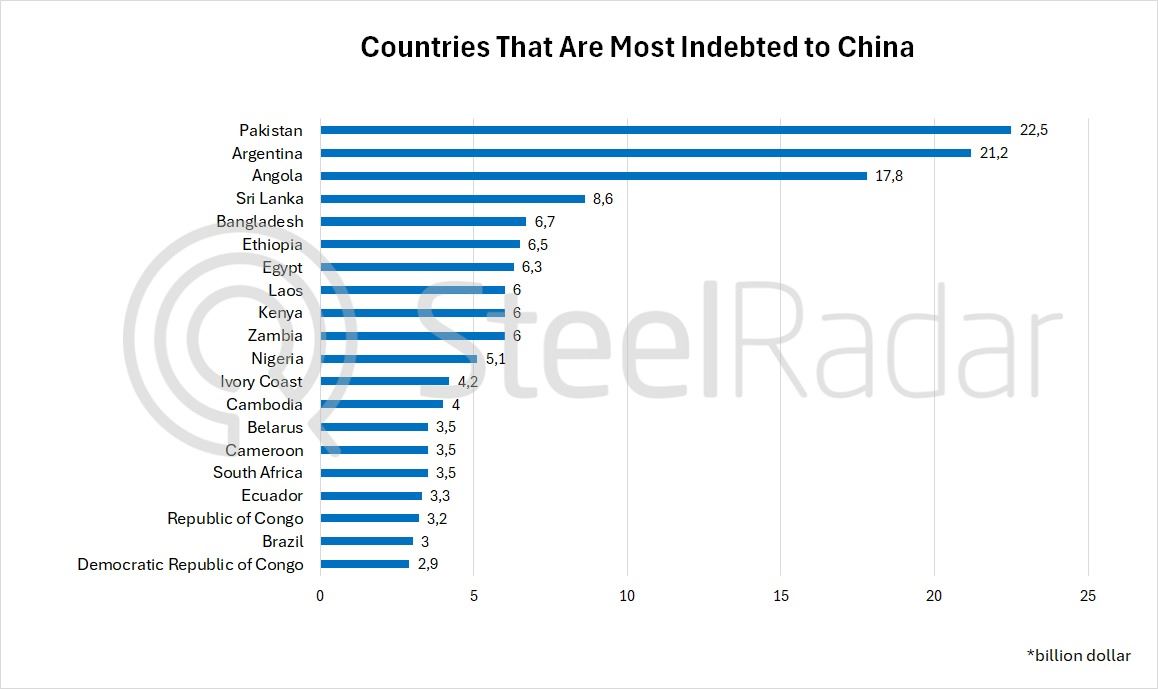
According to World Bank data, 11 of the 20 countries with the highest debt to China in 2023 are located in the African continent. The African country with the highest debt to China is Angola with USD 17.8 billion, followed by Ethiopia with USD 6.5 billion and Egypt with USD 6.3 billion. Zambia, Kenya, Nigeria, Ivory Coast, South Africa, Cameroon, the Republic of Congo and the Democratic Republic of Congo are also among the African countries that owe large amounts to China.
Countries outside Africa include Pakistan (USD 22.5 billion), Argentina (USD 21.2 billion), Sri Lanka (USD 8.6 billion), Bangladesh (USD 6.7 billion) and Laos (USD 6 billion).
“China Meets Africa's Needs in the Most Favorable Conditions”
Koç University Lecturer Dr. Altay Atlı told AA correspondent that large infrastructure projects in Africa under the Belt and Road Initiative are carried out in line with Chinese state policy. Atlı stated, “China acts with the state capitalism model. The financing is provided by Chinese banks and the project is carried out by Chinese companies. This is not accidental or market-based, it is part of Chinese foreign policy.”
Emphasizing that African countries have great infrastructure needs, Atlı stated, “The main reason why most of the countries that owe China are from Africa is that these countries need large projects. China offers favorable financing conditions and completes projects faster. Also, unlike Western countries, it does not impose political or other conditions,”.
Criticism of Debt Trap Debates
Stating that China's investments in Africa are not only for profit, but also within the scope of China's state policy, Atlı stated: “I disagree with the term ‘debt trap’. The countries concerned may have difficulties in making payments, but this applies not only to debts owed to China, but also to debts owed to other countries. China prefers these countries to pay their debts on time. The debt trap narrative is driven more by geopolitical concerns,”.
Emphasizing that the lack of transparency has been criticized and that projects should be evaluated one by one, Atlı added that it does not make sense for China to trap African countries in debt in line with its economic and political interests.
Green Transformation and Shift towards Digitalization
Explaining that China has recently shifted from infrastructure projects in Africa to high value-added but smaller-scale projects such as digitalization and green transformation, Atlı stated, “China is no longer just building physical infrastructure; it is seeking leadership in areas such as artificial intelligence and 5G. Digitalization projects also protect China from the risk of debt default and strengthen China's global position.”
AA









Comments
No comment yet.