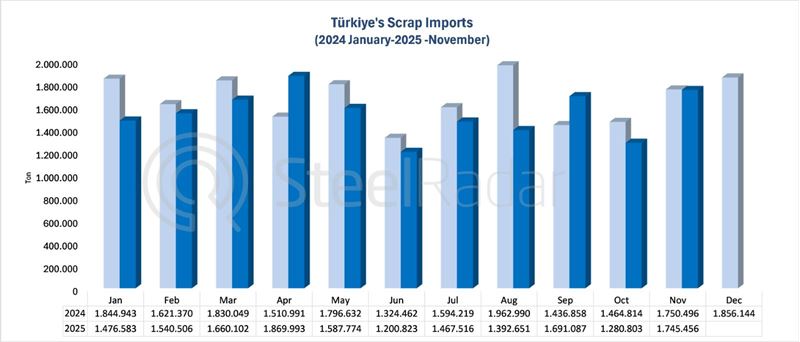
Analysts note that increasing the share of electric arc furnace (EAF) technology in steel production to 15% could reduce the country's carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions by over 160 million tons. This is close to the total carbon footprint of the European Union steel sector. The news was reported by News.Az with reference to Reuters.
China is the world's largest steel producer, accounting for more than half of global crude steel production. But the country lags behind the global average in the adoption of EAF technology, a cleaner production method. While the global EAF production rate stands at 30%, in China it is only around 10%. According to CREA's data, this rate is 71.8% in the US, 58.8% in India and 26.2% in Japan.
CREA analyst Belinda Schaepe stated, “A credible strategy to reduce emissions-intensive production and contain overcapacity will not only solve the industry's structural problems, but also reduce tensions in global trade.”
China produced 1.005 billion tons of crude steel in 2024, about 90% of which came from blast furnaces. Overcapacity in the country's steel industry is causing global prices to fall and trade tensions to escalate as exports surge. On the other hand, high electricity prices, unstable scrap supply and mounting financial losses are among the main factors making it difficult to expand EAF technology in China.








Comments
No comment yet.